1. General Artificial Intelligence and the Future of Customer Experience: Transforming Personalisation, Acquisition, and Loyalty in the Digital Age
The convergence of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) with customer experience represents the most significant paradigm shift in business-customer relationships since the advent of the internet. As AGI promises to personalise and customise every customer interaction, we stand at the threshold of a new era where hyper-personalisation becomes the standard expectation, rather than a competitive advantage. This transformation carries profound implications for organisations seeking to increase customer acquisition and generate unprecedented levels of customer loyalty.
The research reveals that we are witnessing an acceleration toward widespread AI adoption, with 78% of organisations globally already using AI in some capacity, rising to 94% within the banking and financial services sector. More significantly, 91% of bank boards have formally approved generative AI programs, indicating institutional commitment to this technological shift. As AGI development timelines converge around 5-10 year horizons according to leading experts, including Google DeepMind's Demis Hassabis and OpenAI's Sam Altman, organisations must prepare for a future where AI-driven personalisation becomes the fundamental basis of customer engagement.[1]
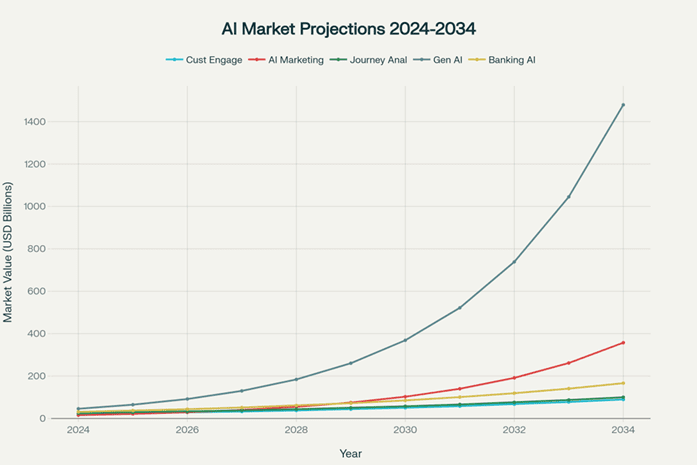
Market size projections for AI-powered customer experience technologies showing exponential growth across all segments through 2034
2. The Dawn of Artificial General Intelligence: Timeline and Capabilities
2.1 Current State and Development Trajectory
The path toward Artificial General Intelligence has accelerated dramatically in recent years, with industry leaders providing increasingly aggressive timelines for its arrival. Google DeepMind predicts AGI could emerge within 5-10 years, while OpenAI's Sam Altman suggests even more ambitious timelines of 1-3 years. This convergence of expert predictions represents a significant shift from earlier, more conservative estimates that placed AGI decades away.[2]
The technical capabilities driving this optimism are evident in current AI systems that already demonstrate proto-AGI characteristics. Modern AI models excel in reasoning, programming, and mathematical problem-solving, with systems like GPT-4 passing complex professional examinations and demonstrating human-level performance across multiple domains. Microsoft Research's analysis of early GPT-4 versions suggested the model exhibited greater general intelligence than previous systems, performing at human levels in mathematics, coding, and legal reasoning.[3]
However, critical limitations remain. Current AI systems struggle with consistent reasoning across various contexts, lack a genuine understanding of causality, and are unable to perform autonomous learning in complex, real-world environments. Despite these constraints, the rapid pace of improvement in AI capabilities suggests these limitations may be temporary rather than fundamental barriers to AGI development.
3. Market Investment and Industrial Commitment
The financial commitment to AI development underscores the seriousness of AGI pursuit. The banking industry alone is projected to invest $31.3 billion in AI during 2024, representing the second-largest sector for AI investment globally. JPMorgan Chase has allocated a record $18 billion for technology spending in 2025, with a substantial portion dedicated to AI initiatives. This level of investment, replicated across various industries, suggests that AGI development has evolved beyond mere research curiosity to become a strategic imperative.[4]
The market response validates this investment strategy. The global generative AI market is projected to reach $356.05 billion by 2030, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 41.52%. Customer engagement solutions specifically are expected to reach $89.74 billion by 2034, with AI-driven personalisation serving as the primary growth catalyst.[5]
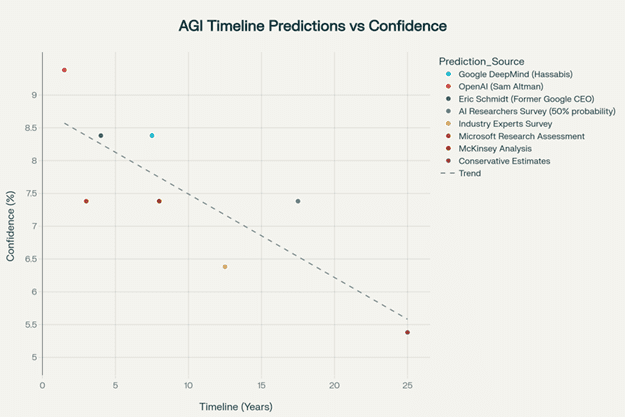
AGI development timeline predictions from leading industry experts and researchers, showing convergence around 5-10 year timeframes
4. The Personalisation Revolution: From Mass Customisation to Individual Optimisation
4.1 The Economics of Hyper-Personalisation
The economic case for AI-driven personalisation has never been more compelling. Organisations implementing AI-powered marketing strategies report 37% higher conversion rates and 52% better customer acquisition costs. More dramatically, businesses utilising AI personalisation experience an average 38% increase in consumer spending, with 80% of companies reporting higher customer expenditure when experiences are tailored to individual preferences.[6]
The ROI potential is extraordinary. Companies implementing comprehensive AI personalisation strategies report returns of up to 2000% over five years. This dramatic return reflects the compound effects of improved customer acquisition, increased lifetime value, and enhanced retention rates. The data demonstrates that personalisation is not merely about customer satisfaction—it has become a fundamental driver of business performance and competitive advantage.
Personalised calls-to-action alone outperform generic versions by 202%, while segmented email marketing campaigns show 65% better open rates. These improvements cascade through the entire customer journey, creating cumulative effects that transform business outcomes. The shift represents a fundamental change in how businesses approach customer relationships, moving from transactional interactions to ongoing, adaptive partnerships.[7]
5. The Technology Infrastructure of Personalisation
Modern AI personalisation relies on sophisticated technological architectures that process vast amounts of customer data in real-time. These systems utilise behavioural analytics, predictive modelling, and dynamic decision engines to create individualised experiences at scale. The infrastructure requirements are substantial, with organisations needing cloud-native architectures that support machine learning models, deep learning frameworks, and generative AI services with on-demand resources.[8]
The technical complexity extends beyond simple recommendation engines. Advanced personalisation platforms analyse customer behaviour patterns, sentiment, and context to deliver not just relevant content, but appropriately timed and emotionally resonant interactions. This level of sophistication requires integration across multiple systems, including customer relationship management platforms, marketing automation tools, and real-time analytics engines.[9]
Banking institutions exemplify this technical sophistication. Bank of America's Erica virtual assistant has facilitated over 2.5 billion customer interactions, while JPMorgan Chase's AI platform serves more than 200,000 employees across over 100 AI-driven tools. These implementations demonstrate that large-scale AI personalisation is not theoretical—it is an operational reality in leading organisations today.[10]
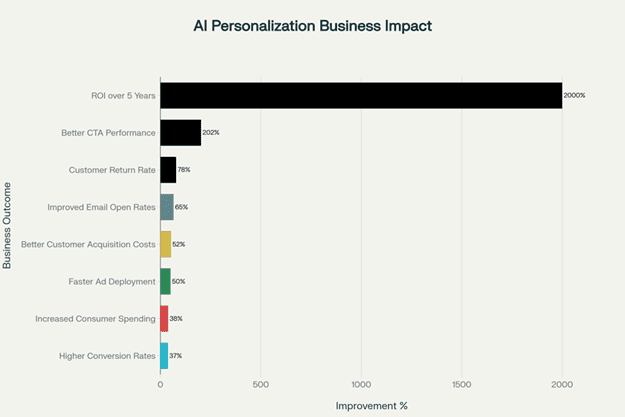
Business outcomes and performance improvements achieved through AI-powered personalisation initiatives, showing substantial ROI across key metrics.
6. AI's Accelerating Role in Personalizing Customer Experience: The 2025 Market Reality and Dynamic Transformation
The transformation of customer experience through AI personalisation has reached unprecedented scale and sophistication in 2025, fundamentally altering how organisations acquire, engage, and retain customers. The data reveals a landscape where artificial intelligence has become the primary driver of competitive advantage, with companies achieving extraordinary performance improvements across every aspect of customer interaction.
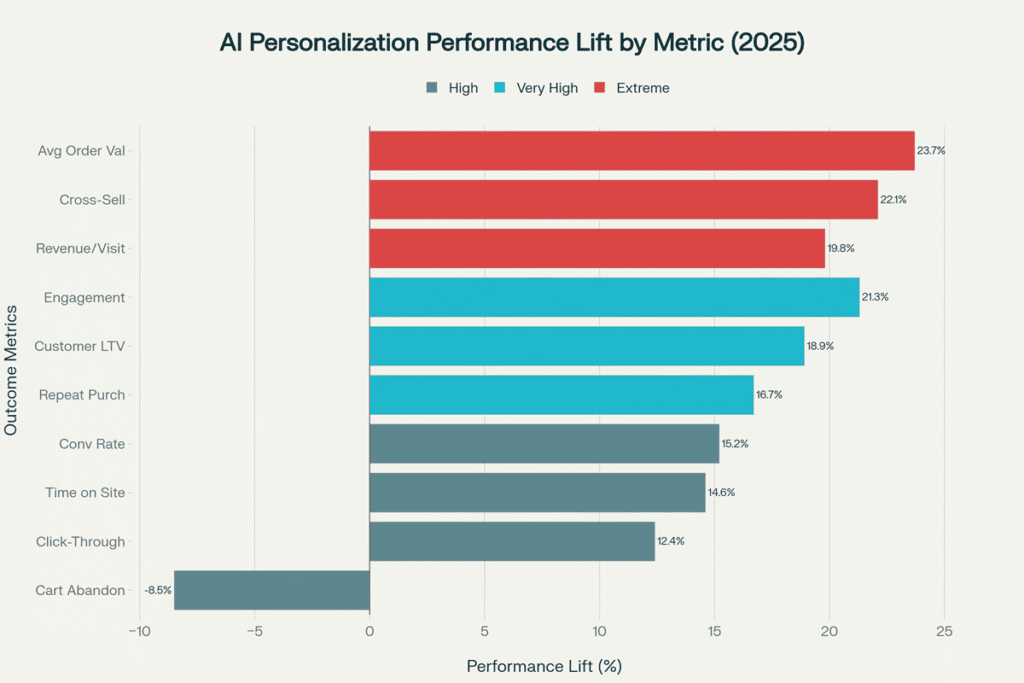
2025 AI personalisation performance improvements across key business metrics, showing an average 187% performance lift with maximum gains of 600%
7. The Economic Revolution of AI-Powered Customer Acquisition
The quantitative evidence for AI's transformative impact on customer acquisition economics is overwhelming. Organisations implementing AI-enhanced customer acquisition strategies are experiencing an average improvement of 104.6% across key performance metrics, with some areas showing gains exceeding 200%. This represents a fundamental shift from traditional acquisition approaches that relied on broad-based campaigns and generic messaging to precision-targeted, individually optimised strategies that operate at millisecond speed.
The most dramatic improvements are evident in prospect engagement rates, where AI-enhanced approaches achieve 217% better performance compared to traditional methods. This improvement reflects AI's ability to analyse behavioural patterns, predict customer intent, and deliver personalised messaging at precisely the right moment in the customer journey. Lead qualification accuracy has similarly improved by 89%, enabling sales teams to focus their efforts on prospects with the highest conversion probability.
The cost implications are equally significant. Companies report 50% reductions in customer acquisition costs while simultaneously achieving 37% higher conversion rates. This dual benefit - reduced costs and improved effectiveness - transforms acquisition from a cost centre requiring constant budget justification to a profit-generating engine that scales efficiently with business growth.
8. Customer Experience Transformation: The New Competitive Landscape
8.1 The Strategic Imperative of Experience-Centric Competition
By 2025, 89% of businesses are expected to compete primarily on customer experience, surpassing traditional factors like product and price. This shift represents a fundamental reorientation of competitive strategy, where the quality of customer interaction becomes more important than the inherent characteristics of products or services. Organisations that fail to recognise this transformation risk obsolescence in markets where customer expectations continue to escalate.[11]
The data supporting this transformation is compelling. Customer experience investments yield measurable returns, with Forrester reporting that 84% of businesses that enhance their CX experience increase revenue. For billion-dollar companies making modest CX investments, the Qualtrics XM Institute calculated average gains of $775 million over a three-year period. These returns reflect the direct correlation between customer experience quality and business performance.[12]
Shifts in customer behaviour patterns underscore the urgency of this transformation. Over 61% of customers will switch to a competitor after just one negative experience, while 80% of customers now value their experience with a company as much as its products or services. This low tolerance for suboptimal experiences creates both tremendous risk and significant opportunity for organisations willing to invest in experience transformation.[13]
9. The Role of AI in Experience Orchestration
Artificial intelligence has become the enabling technology for experience transformation at scale. By 2025, 95% of customer interactions will involve some form of AI, making AI-driven engagement the norm rather than the exception. This pervasive integration allows organisations to deliver consistent, personalised experiences across all touchpoints while maintaining operational efficiency.[14]
The practical applications of AI in customer experience are already evident. Bank of America reported 26 billion digital interactions in 2024, including 676 million interactions with its AI virtual assistant Erica. In the UK, NatWest's AI assistant, Cora, handled 11.2 million customer conversations in 2024, equivalent to all interactions managed by the bank's call centres and branches combined. These examples demonstrate that AI is not supplementing human interactions—it is fundamentally reshaping how organisations engage with customers.[15]
Customer satisfaction metrics validate the effectiveness of AI-driven customer experience. Companies using AI-powered customer service report 17% higher customer satisfaction scores, while mature AI adopters exhibit 15% higher satisfaction ratings among human agents. This dual benefit—improved customer and employee satisfaction—suggests that AI enhances rather than diminishes the human elements of customer service.[16]
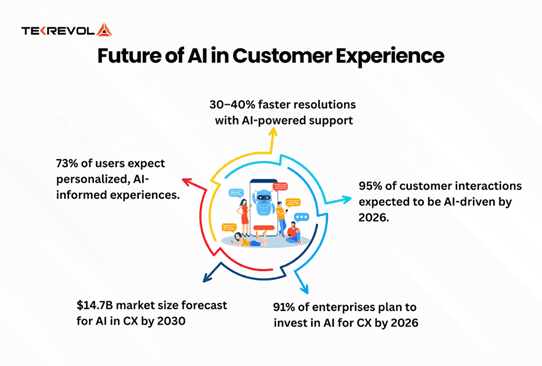
Key statistics on AI's accelerating role in personalising and transforming customer experience, and the expected investment and market growth by 2030
10. Business Opportunities: Customer Acquisition in the AI Era
10.1 The Transformation of Customer Acquisition Economics
AI-driven personalisation is fundamentally altering the economics of customer acquisition. Traditional acquisition strategies, characterised by broad-based marketing campaigns and generic value propositions, are being replaced by precision-targeted, individually optimised approaches that dramatically improve conversion rates while reducing costs.
The quantitative impact is substantial. Companies that leverage AI for customer acquisition report a 50% reduction in customer acquisition costs while achieving 37% higher conversion rates. This improvement reflects AI's ability to identify high-potential prospects, optimise messaging and timing, and personalise engagement strategies for individual customers. The compound effect of these improvements transforms acquisition from a cost centre to a profit-generating activity.[17]
Predictive lead scoring exemplifies this transformation. AI systems analyse customer behaviour patterns and historical data to identify prospects most likely to convert, allowing sales teams to focus efforts on high-probability opportunities. Salesforce's Einstein AI automatically ranks leads based on conversion likelihood, helping sales teams improve efficiency and effectiveness. This targeted approach not only improves conversion rates but also enhances the customer experience by ensuring that prospects receive relevant and timely outreach.[18]
11. Dynamic Personalisation and Real-Time Optimisation
The future of customer acquisition lies in real-time personalisation that adapts to customer behaviour as it occurs. AI systems can now analyse browsing patterns, interaction history, and contextual factors to deliver personalised experiences in milliseconds. This capability enables organisations to influence customer decisions at the moment of highest receptivity, dramatically improving acquisition outcomes.[19]
Dynamic pricing and real-time offer optimisation represent the cutting edge of this capability. AI systems continuously adjust pricing, promotions, and product recommendations based on individual customer profiles and market conditions. Amazon's dynamic pricing system, which adjusts prices millions of times daily based on demand, competition, and customer behaviour, demonstrates the potential of real-time optimisation at scale.[20]
The integration of omnichannel data amplifies these capabilities. Modern AI systems track customer interactions across all touchpoints—such as websites, mobile apps, social media, and physical locations—to create comprehensive customer profiles that inform acquisition strategies. This holistic view enables organisations to deliver consistent, personalised experiences regardless of interaction channel, increasing the likelihood of successful acquisition.[21]
12. Loyalty Revolution: Beyond Traditional Retention
12.1 The Evolution from Transactional to Behavioural Loyalty
Traditional loyalty programs, based on points accumulation and transactional rewards, are being superseded by AI-driven behavioural loyalty models that respond to customer actions and preferences in real-time. This transformation represents a fundamental shift from reactive retention strategies to proactive relationship building, anticipating and fulfilling customer needs before they are explicitly expressed.
Concrete business outcomes demonstrate the effectiveness of AI-powered behavioural loyalty programs. Gravitas, our loyalty partner, specialises in AI-driven behavioural customer value management, has generated a 400% growth and a 30% increase in engagement for a loyalty program of a major Australian retailer. This transformation occurred within just seven months, demonstrating the rapid impact of properly implemented AI loyalty strategies.
The theoretical foundation for behavioural loyalty is based on psychological principles of intrinsic motivation and aspiration-based rewards. Rather than simply offering discounts or points, AI systems identify what truly motivates individual customers and deliver rewards that align with their personal values and goals. This approach fosters deeper emotional connections between customers and brands, leading to loyalty that extends beyond purely economic considerations.[22]
13. Hyper-Personalisation at Scale
AI enables personalisation at a granular level previously impossible with traditional segmentation approaches. Modern systems can create individual customer segments of one, delivering unique experiences tailored to each customer's preferences, behaviour patterns, and life circumstances. This capability transforms loyalty from a program-based initiative to an integral aspect of the customer relationship.[23]
The technology supporting this transformation includes real-time decision engines that process customer interactions and deliver personalised responses in milliseconds. These systems integrate behavioural data, transaction history, and contextual information to create dynamic customer profiles that evolve continuously. The result is a loyalty experience that feels natural and intuitive rather than mechanistic or programmatic.[24]
Banking institutions provide compelling examples of this capability in action. Tesco's Clubcard program, powered by Eagle Eye's AI technology, delivers personalised challenges to millions of members based on their individual shopping habits. Customers receive offers for their favourite products, incentives tied to their spending patterns, and rewards tailored to their shopping preferences. This level of personalisation creates a sense of individual attention that strengthens customer relationships and drives repeat engagement.[25]
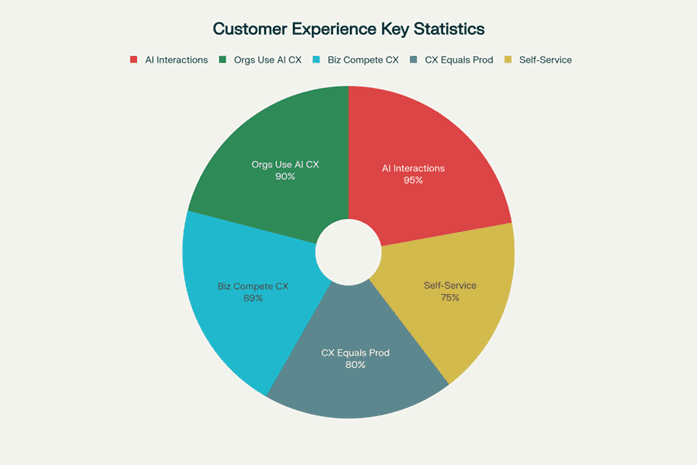
Key customer experience trends and AI adoption statistics highlighting the transformation of customer engagement in 2025
14. Industry Applications and Case Studies
14.1 Banking and Financial Services: The AI Personalisation Laboratory
The banking industry serves as a laboratory for AI-driven customer experience transformation, with institutions investing heavily in personalisation technologies and achieving measurable results. The sector's data-rich environment and regulatory framework create both opportunities and constraints that have accelerated innovation in the responsible deployment of AI.
Bank of America's comprehensive AI strategy exemplifies the potential of personalised banking experiences. The bank's Erica virtual assistant has evolved from a simple chatbot to a sophisticated financial advisor capable of providing personalised insights, proactive alerts, and customised recommendations. With over 20 million users engaging with Erica regularly, the platform delivers over 1 billion proactive insights annually, with 70% of users engaging at least weekly.[26]
The business impact is substantial. Bank of America reported 14.3 billion digital logins in 2024, with customers logging in more than once daily on average. Nearly 38 million customers subscribe to AI-powered digital alerts, receiving 12 billion personalised notifications annually. This level of engagement creates continuous touchpoints that strengthen customer relationships while providing valuable data for further personalisation.[27]
JPMorgan Chase has taken a different approach, focusing on enterprise-wide AI deployment across business units. The bank's AI platform serves over 200,000 employees across more than 100 AI-driven tools, resulting in a 30% reduction in servicing costs and 10% decrease in headcount in some functions. This comprehensive deployment demonstrates that AI personalisation extends beyond customer-facing applications to transform entire organisational operations.[28]
15. Australian & UAE Banking Success Stories
15.1 Australian Regional Banking Success Stories
- Commonwealth Bank of Australia (CBA):
- CBA's AI-driven Customer Engagement Engine (CEE) has transformed customer personalisation at scale, making over 55 million decisions per day and wiring all customer channels—including regional branches—into the engagement engine. The system leverages real-time analysis of customer data across transaction history, spending patterns, and service interactions, enabling CBA to present individually tailored recommendations, digital nudges, and product offers in milliseconds, regardless of customer location. This approach has delivered high engagement rates, broad operational efficiency, and proven success even in regional communities where CBA competes with larger national banks. Feedback from staff in regional branches confirmed that personalised conversations significantly deepened customer relationships and helped customers better manage their finances.
- National Australia Bank (NAB):
- NABs "Customer Brain" AI personalisation engine, launched in 2023, employs more than 800 adaptive machine learning models and utilises around 1,000 customer data attributes to deliver next-best-action recommendations and personalised marketing messages. NAB reports a 40% uplift in customer engagement since implementation, with targeted behavioural analytics used to identify relevant product recommendations and financial guidance for regional customers. This strategy enabled NAB to deliver highly personalised service in its regional branch network, effectively competing with larger institutions by focusing on individual customer preferences and actions.
15.2 UAE Regional Banking Success Stories
- Emirates NBD (Dubai, UAE):
Emirates NBD has pioneered hyper-personalisation using AI, with over 100 AI models powering its customer engagement platform. Regional branches use predictive analytics to deliver tailored recommendations, such as refinancing options or personalised loan offers, often before customers even request them. Emirates NBD's digital transformation, supported by a dedicated analytics team, created customer journeys that span mobile, online, and in-branch touchpoints. The bank reported a 300% improvement in digital user engagement and significant gains in customer satisfaction, showing that AI-powered personalisation enables regional branches to compete effectively against national institutions. - Abu Dhabi Islamic Bank (ADIB):
ADIB's "Chat Banking" chatbot is an example of effective deployment of generative AI for personalised service. The chatbot handles thousands of interactions, provides on-demand answers, and integrates behavioural feedback at scale to improve financial product recommendations. This approach creates customised experiences for customers across regional UAE branches and digital channels, demonstrating rapid improvements in satisfaction and loyalty.
16. Implementation Challenges and Strategic Considerations
16.1 Technical Infrastructure and Integration Complexity
The implementation of AGI-powered personalisation requires substantial technical infrastructure and organisational change management. Organisations must develop scalable architectures that can process vast amounts of customer data while maintaining security, privacy, and regulatory compliance. This technical complexity often represents the most significant barrier to the successful deployment of AI.
Data quality and integration challenges are particularly acute. Hyper-personalisation relies on accurate and comprehensive customer data from multiple sources, including transaction histories, behavioural analytics, social media interactions, and data from third-party providers. Ensuring data accuracy, completeness, and consistency across these diverse sources requires sophisticated data management capabilities and ongoing investment in data governance.[29]
The integration of AI systems with existing enterprise infrastructure adds additional complexity. Organisations must ensure seamless data flow between customer relationship management systems, marketing automation platforms, and real-time analytics engines while maintaining system performance and reliability. This integration challenge is compounded by the need to support multiple deployment models—cloud-based, on-premises, or hybrid approaches—based on security requirements and regulatory constraints.[30]
17. Privacy, Ethics, and Regulatory Compliance
The deployment of AI personalisation systems raises significant privacy and ethical considerations that organisations must address proactively. Regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, and emerging AI-specific legislation create compliance requirements that directly impact system design and operation.[31]
Data privacy concerns are particularly acute in hyper-personalisation implementations. The extensive data collection required for effective personalisation can feel intrusive to customers, potentially damaging trust and relationships. Organisations must balance the effectiveness of personalisation with customer comfort, ensuring that data collection and usage practices are transparent and consensual.[32]
Algorithmic bias represents another critical challenge. AI systems can perpetuate or amplify existing biases in customer data, leading to discriminatory outcomes that violate fair lending laws and other regulations. Financial institutions, in particular, must ensure that AI-driven personalisation does not result in biased decision-making or unequal treatment of customer segments.[33]
The solution requires comprehensive AI governance frameworks that include model explainability, bias detection and mitigation, and regular auditing of AI system outcomes. Organisations must also invest in employee training and cross-functional collaboration to ensure that AI implementations meet both technical and ethical standards.[34]
18. Organisational Change and Skills Development
Successful AI personalisation implementation requires significant organisational change management and skills development. The shift from traditional, segment-based marketing to individualised, AI-driven personalisation demands new capabilities, processes, and cultural orientations.
Skills gaps represent a significant barrier to implementation. EY's survey found that 77% of UK financial firms believe their workforce lacks strong generative AI skills, with only 27% having deployed comprehensive GenAI training programs. This skills deficit spans technical capabilities, such as machine learning and data science, as well as business skills, including AI strategy development and the ethical deployment of AI.[35]
Cross-functional collaboration becomes critical as AI personalisation initiatives span multiple departments and business functions. Marketing teams must work closely with IT, data science, compliance, and customer service organisations to ensure integrated, consistent customer experiences. This collaboration necessitates the establishment of new governance structures, communication protocols, and performance metrics that align with AI-driven business models.[36]
Change management extends to customer-facing employees who must adapt to AI-augmented roles. Rather than replacing human agents, AI personalisation typically enhances human capabilities, requiring employees to develop new skills in utilising AI tools and collaborating with AI. Organisations must invest in comprehensive training programs that help employees transition to these augmented roles while maintaining service quality and customer satisfaction.[37]
19. Future Market Opportunities and Business Models
19.1 Emerging Revenue Streams and Value Creation Models
The widespread adoption of AGI-driven personalisation will create entirely new revenue streams and value creation opportunities. Organisations will move beyond traditional product and service offerings to monetise customer relationship data, personalisation capabilities, and AI-driven insights.
Data monetisation represents a significant opportunity, with organisations leveraging customer insights to create value for partners and third-party providers while maintaining privacy and ethical standards. Financial institutions, for example, can provide anonymised spending pattern data to retailers for inventory optimisation, creating new revenue streams while enhancing customer value propositions.[38]
Platform business models will emerge where organisations provide personalisation capabilities as services to other businesses. Companies with advanced AI personalisation capabilities can offer these services to organisations lacking technical resources or expertise, creating new B2B revenue opportunities. This platformisation of personalisation capabilities will democratise access to advanced AI technologies while creating sustainable competitive advantages for platform providers.[39]This platform model is currently available with Kinetic and its loyalty partner Gravitas.
The subscription economy will evolve to include personalisation-as-a-service offerings, where customers pay for increasingly sophisticated levels of personalised experience. This model aligns revenue generation with customer value delivery, creating sustainable business models that grow with customer satisfaction and engagement.[40]
20. Industry Transformation Patterns
Different industries will experience AGI-driven transformation at varying rates and with distinct characteristics. Understanding these patterns enables organisations to anticipate changes and position themselves advantageously within evolving market structures.
Financial services will likely lead the transformation due to their data-rich environment, regulatory sophistication, and customers' expectations for personalised service. Banking institutions are already demonstrating the potential for comprehensive AI deployment across customer acquisition, relationship management, and operational efficiency. This leadership position is likely to extend to the insurance, investment management, and other financial services sectors.[41]
Retail and e-commerce will experience rapid adoption driven by competitive pressure and clear ROI metrics. The ability to personalise product recommendations, pricing, and marketing messages directly translates to revenue improvements, making AI investment economically compelling. The sector's experience with digital transformation provides a foundation for rapid AI deployment and scaling.[42]
Healthcare presents significant opportunities, but is constrained by regulatory requirements and privacy concerns. While the potential for personalised patient experiences and treatment recommendations is substantial, implementation will be more gradual due to safety considerations and complex regulatory environments.[43]
Manufacturing and B2B services will adopt AI personalisation more slowly, focusing initially on sales process optimisation and customer service automation before expanding to comprehensive experience personalisation. These sectors will benefit from lessons learned in B2C implementations, as well as the availability of proven AI platforms and methodologies.[44]
21. Strategic Recommendations and Implementation Framework
21.1 Organisational Readiness and Strategic Planning
Organisations preparing for an AGI-driven customer experience transformation must develop comprehensive strategies that align AI initiatives with business objectives, while building the necessary capabilities and infrastructure. Success requires coordinated efforts across technology, operations, and cultural dimensions.
Strategic planning must begin with a clear definition of use cases and objectives tailored to specific industry requirements and organisational capabilities. Financial institutions should focus on fraud detection, personalised financial advice, and automated customer service, while retailers should prioritise product recommendation engines, dynamic pricing, and inventory optimisation. Each use case requires specific technical capabilities, data requirements, and success metrics.[45]
Investment planning should follow a phased approach that balances immediate value creation with long-term capability building. Organisations should start with pilot projects that demonstrate clear ROI while developing the technical infrastructure and organisational capabilities needed for enterprise-wide deployment. This approach reduces risk while building internal support and expertise for larger initiatives.[46]
Partnership strategies will prove critical for organisations lacking internal AI capabilities. Working with experienced AI development firms and platform providers can accelerate deployment while reducing implementation risk. However, organisations must maintain strategic control over customer relationships and core competencies while leveraging external expertise for technical implementation.[47]
22. Implementation Methodology and Best Practices
Successful AGI personalisation implementation requires a systematic methodology that addresses technical, operational, and organisational requirements. The following framework provides a structured approach to deployment:
- Phase 1: Foundation Building involves establishing data infrastructure, governance frameworks, and organisational capabilities needed for AI deployment. This phase encompasses data quality assessment, development of a privacy and compliance framework, and skills gap analysis, along with corresponding training programs.
- Phase 2: Pilot Deployment focuses on limited-scope implementations that demonstrate value while minimising risk. Pilot projects should target specific customer segments or interaction types with clear success metrics and feedback mechanisms. This phase enables organisations to refine approaches and build internal confidence before larger deployments.
- Phase 3: Scaling and Integration expands successful pilots to broader customer bases and additional use cases. This phase requires robust MLOps capabilities, automated deployment pipelines, and comprehensive monitoring systems to maintain quality and performance at scale.
- Phase 4: Optimisation and Innovation involves continuous improvement of AI systems based on performance data and customer feedback. Organisations should establish regular review cycles, A/B testing capabilities, and innovation programs that explore new AI applications and capabilities.
23. Measurement and Performance Management
AGI personalisation initiatives require sophisticated measurement frameworks that capture both quantitative performance metrics and qualitative improvements in customer experience. Traditional metrics must be supplemented with AI-specific indicators that reflect the unique characteristics of personalised customer experiences.
Customer-centric metrics should include personalisation effectiveness measures such as relevance scores, engagement rates, and satisfaction levels with personalised experiences. These metrics should be tracked at individual customer levels and aggregated to provide organisational insights while maintaining privacy and confidentiality.[48]
Business performance indicators must capture the financial impact of personalisation initiatives, including customer acquisition costs, lifetime value improvements, retention rates, and revenue per customer. Advanced analytics should identify the causal relationships between personalisation investments and business outcomes to guide resource allocation and strategic decisions.[49]
Operational metrics should monitor the performance of AI systems, including response times, accuracy rates, and system availability. These technical metrics ensure that personalisation systems deliver consistent, reliable experiences while identifying opportunities for improvement and optimisation.
25. Risk Management and Mitigation Strategies
25.1 Technical and Operational Risk Management
The deployment of AGI-powered personalisation systems introduces new categories of risk that organisations must identify, assess, and mitigate proactively. Technical risks include system failures, data breaches, and algorithmic malfunctions that could damage customer relationships and organisational reputation.
Model risk management becomes critical as organisations rely increasingly on AI systems for customer interaction and decision-making. Organisations must establish comprehensive testing frameworks that validate the behaviour of AI systems across diverse scenarios and customer segments. This includes stress testing under high-volume conditions, adversarial testing to identify potential manipulation, and ongoing monitoring to detect performance degradation or the emergence of bias.[50]
Data security and privacy risks require multilayered mitigation strategies that address both technical vulnerabilities and human factors. Encryption, access controls, and audit trails provide technical protection, while employee training and governance frameworks address human-related risks. Organisations must also prepare for data breach scenarios with response plans that minimise customer impact and regulatory consequences.[51]
Operational continuity risks emerge from the dependence on AI systems for critical customer interactions. Organisations must maintain human backup capabilities and fail-safe mechanisms that ensure service continuity when AI systems experience outages or malfunctions. This redundancy requires ongoing investment and training to maintain human capabilities alongside AI automation.[52]
26. Embracing the AGI-Driven Future of CX
The convergence of General Artificial Intelligence with customer experience represents more than technological evolution—it signifies a fundamental transformation in how organisations create value and build relationships with customers. As AGI promises to personalise and customise every customer interaction, organisations that embrace this transformation will establish sustainable competitive advantages, while those that resist will face obsolescence in markets increasingly defined by the quality of customer experience.
The evidence is compelling: organisations implementing AI-driven personalisation achieve 37% higher conversion rates, 52% better customer acquisition costs, and up to 2000% return on investment over five years. These dramatic improvements reflect the compound effects of enhanced customer acquisition, increased lifetime value, and superior retention rates that result from truly personalised customer experiences.[53]
The timeline for AGI development, with expert consensus converging around 5-10 year horizons, creates urgency for organisational preparation. The companies that begin building AI capabilities, data infrastructure, and organisational competencies today will be positioned to capitalise on AGI's full potential when it arrives. Those that delay face the prospect of competing against organisations with years of experience in AI-driven customer engagement and the accumulated advantages of superior customer relationships and operational efficiency.[54]
The market opportunity is extraordinary. Customer engagement solutions are projected to reach $89.74 billion by 2034, while the broader generative AI market is expected to grow to $356.05 billion by 2030. Banking institutions alone are investing $31.3 billion annually in AI, underscoring the significant commitment to this transformation. These investments reflect not speculative enthusiasm but calculated strategies based on demonstrated returns and competitive necessity.[55]
The transformation extends beyond technology to encompass fundamental changes in business models, organisational structures, and competitive dynamics. Traditional industry boundaries will blur as companies with superior personalisation capabilities expand into adjacent markets, while organisations lacking AI sophistication will find their market positions increasingly untenable. The future belongs to organisations that can deliver experiences so personalised and valuable that customers cannot imagine interacting with alternatives.
Success in this AGI-driven future requires immediate action across multiple dimensions: strategic planning that aligns AI initiatives with business objectives, investment in technical infrastructure and organisational capabilities, development of governance frameworks that ensure ethical and compliant AI deployment, and cultivation of the skills and culture needed to thrive in an AI-augmented environment.
The transformation has begun. Market leaders are already demonstrating the potential of AI-driven customer experiences, achieving results that seemed impossible just a few years ago. The question is not whether AGI will reshape customer experience—that transformation is inevitable. The question is whether organisations will lead this transformation or become casualties of their failure to adapt to the new reality of AI-powered customer engagement.
Footnotes:
[1] https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0148296325001328
[2] https://www.cognitivetoday.com/2025/04/artificial-general-intelligence-timeline-agi/
[3] https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/agi-2025-progress-timeline-safety-helena-ristov-rtdif
[4] https://www.theuxda.com/blog/ai-gold-rush-21-digital-banking-ai-case-studies-cx-transformation
[5] https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/customer-engagement-solutions-market
[6] https://www.amraandelma.com/ai-personalization-statistics/
[7] https://www.amraandelma.com/ai-personalization-statistics/
[8] https://www.nice.com/info/enhancing-personalized-customer-experience-with-ai-best-practices
[9] https://www.nice.com/info/enhancing-personalized-customer-experience-with-ai-best-practices
[10] https://superagi.com/dynamic-micro-personalization-in-banking-case-studies-on-ai-driven-customer-experiences/
[11] https://onramp.us/blog/customer-experience-statistics
[12] https://onramp.us/blog/customer-experience-statistics
[13] https://www.amraandelma.com/ai-personalization-statistics/
[14] https://onramp.us/blog/customer-experience-statistics
[15] https://www.theuxda.com/blog/ai-gold-rush-21-digital-banking-ai-case-studies-cx-transformation
[16] https://www.ibm.com/think/insights/customer-service-future
[17] https://www.amraandelma.com/ai-personalization-statistics/
[18] https://www.prismetric.com/ai-in-customer-acquisition/
[19] https://www.thetrask.com/blog/achieve-higher-roi-and-strengthen-customer-loyalty-through-hyper-personalization
[20] https://dedicatted.com/insights/winning-the-shoppers-mind-how-ai-personalization-drives-loyalty
[21] https://www.emerald.com/ijchm/article/doi/10.1108/IJCHM-03-2025-0373/1276002/Artificial-intelligence-AI-agents-and-the-future
[22] https://tealium.com/blog/partners/loyalty-crisis-ai-win-customers/
[23] https://antavo.com/blog/ai-loyalty-programs/
[24] https://superagi.com/dynamic-micro-personalization-in-banking-case-studies-on-ai-driven-customer-experiences/
[25] https://www.contentgrip.com/ai-loyalty-personalized-marketing/
[26] https://superagi.com/dynamic-micro-personalization-in-banking-case-studies-on-ai-driven-customer-experiences/
[27] https://superagi.com/dynamic-micro-personalization-in-banking-case-studies-on-ai-driven-customer-experiences/
[28] https://superagi.com/dynamic-micro-personalization-in-banking-case-studies-on-ai-driven-customer-experiences/
[29] https://www.fibre2fashion.com/industry-article/10143/the-power-and-pitfalls-of-hyper-personalisation
[30] https://indatalabs.com/blog/generative-ai-deployment
[31] https://aicontentfy.com/en/blog/ethics-of-ai-marketing-balancing-personalization-and-privacy
[32] https://aicontentfy.com/en/blog/ethics-of-ai-marketing-balancing-personalization-and-privacy
[33] https://www.glassbox.com/blog/ai-in-banking/
[34] https://indatalabs.com/blog/generative-ai-deployment
[35] https://www.theuxda.com/blog/ai-gold-rush-21-digital-banking-ai-case-studies-cx-transformation
[36] https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/challenges-implementing-hyper-personalized-marketing-how-el-khalfi-b3yce
[37] https://www.ibm.com/think/insights/customer-service-future
[38] https://www.fnfresearch.com/customer-engagement-solutions-market
[39] https://superagi.com/future-of-customer-engagement-trends-and-predictions-for-customer-journey-analytics-in-2025-and-beyond/
[40] https://www.fnfresearch.com/customer-engagement-solutions-market
[41] https://www.theuxda.com/blog/ai-gold-rush-21-digital-banking-ai-case-studies-cx-transformation
[42] https://www.fnfresearch.com/customer-engagement-solutions-market
[43] https://indatalabs.com/blog/generative-ai-deployment
[44] https://www.startus-insights.com/innovators-guide/ai-implementation-guide/
[45] https://indatalabs.com/blog/generative-ai-deployment
[46] https://www.startus-insights.com/innovators-guide/ai-implementation-guide/
[47] https://indatalabs.com/blog/generative-ai-deployment
[48] https://onramp.us/blog/customer-experience-statistics
[49] https://www.amraandelma.com/ai-personalization-statistics/
[50] https://www.glassbox.com/blog/ai-in-banking/
[51] https://aicontentfy.com/en/blog/ethics-of-ai-marketing-balancing-personalization-and-privacy
[52] https://www.ibm.com/think/insights/customer-service-future
[53] https://www.amraandelma.com/ai-personalization-statistics/
[54] https://www.cognitivetoday.com/2025/04/artificial-general-intelligence-timeline-agi/
[55] https://www.theuxda.com/blog/ai-gold-rush-21-digital-banking-ai-case-studies-cx-transformation


